Why European Hornets are scary? - European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings
Editor's Notes: European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings has published today date. European Hornets are one of the most common types of hornets in Europe, and their stings can be painful. Understanding the biology of these insects can help you to prevent being stung and to treat stings if they do occur.
We analyzed and dug up information, made European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings we put together this European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key differences or Key takeways
| Characteristics | European Hornets |
| Size | 1.5-2.5 cm |
| Color | Brown or black with yellow markings |
| Nests | In trees, shrubs, or other sheltered areas |
| Diet | Insects |
| Stings | Painful, and can be dangerous for people who are allergic |
Transition to main article topics
FAQ
In this section, we address commonly asked questions regarding European hornets, their biology, and the prevention of stings. By providing clear and informative answers, we aim to empower you with the knowledge necessary to minimize the risks associated with these insects.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Europeanhornet-208b2fa4e57645fd9c52797c236b88ef.jpg)
Asian Giant Hornets (or Killer Hornets) and How to Identify Them - Source www.thespruce.com
Question 1: Are European hornets considered aggressive?
While European hornets have the potential to be defensive when their nest is threatened, they typically exhibit a docile nature. They are less inclined to sting compared to other species of wasps and hornets.
Question 2: What are the common triggers for hornet stings?
Hornet stings usually occur when the insect feels threatened or perceives a potential danger to its colony. Disturbing their nest, inadvertently bumping into them, or accidentally stepping on them can trigger a defensive response.
Question 3: Can hornet stings be life-threatening?
In most cases, hornet stings result in localized pain, swelling, and redness. However, for individuals with severe allergies or specific health conditions, multiple stings can pose a significant risk. Anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction, requires immediate medical attention.
Question 4: What measures can be taken to prevent hornet stings?
There are several effective measures to minimize the risk of hornet stings. These include avoiding wearing bright or floral clothing, refraining from using perfumes or scented products, sealing off potential entry points in your home and outbuildings, and maintaining a clean environment free of food scraps and sugary substances.
Question 5: What should be done if stung by a European hornet?
In the event of a hornet sting, it is crucial to remain calm and avoid panicking. Remove the stinger promptly using a pair of tweezers or a plastic card. Clean the affected area with soap and water to prevent infection. Apply a cold compress to reduce pain and swelling. If severe pain or allergic reactions develop, seek medical attention immediately.
Question 6: Is it beneficial to kill European hornets?
While it may be tempting to eliminate hornets on your property, indiscriminate killing is not recommended. Hornets play a beneficial role in the ecosystem as predators of other insects and pollinators. Consider humane pest control methods or seek professional assistance if hornet activity becomes a problem.
By understanding the nature and behaviors of European hornets, we can effectively reduce the likelihood of painful encounters and ensure a safe and harmonious coexistence.
For further information about European hornets and their management, consult reputable pest control professionals or local authorities.
Tips
To prevent the risk of being stung by a European Hornet, consider these proactive and responsive measures.
Tip 1: Be cautious around areas where you suspect or observe hornets, such as their nests or foraging grounds. Keep a safe distance and avoid disturbing them.
Tip 2: Avoid wearing dark or bright-colored clothing and strong perfumes when outdoors, as hornets are attracted to these. Wear light-colored, loose-fitting clothing that covers your skin.
Tip 3: Seal cracks and holes in walls, eaves, and other areas around your home to prevent hornets from entering and nesting.
Tip 4: Keep your yard free of fallen fruit and sugary spills. These attract hornets and other stinging insects.
Tip 5: If you encounter a nest, do not attempt to remove it yourself. Contact a professional pest control service for safe and effective removal.
Tip 6: If stung, remain calm. Remove the stinger by scraping it off with a fingernail or dull object. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain.
For more comprehensive information on the biology and prevention of stings from European Hornets, refer to the detailed article European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings .
By following these tips, you can reduce the chances of encountering European Hornets and minimize the risk of painful stings.
European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings
European hornets (Vespa crabro) are social wasps native to Europe. They are known for their painful stings and aggressive behavior. Understanding their biology and taking preventive measures against their stings are important for reducing the risks associated with these insects.
New Infection Prevention News | Voice for Infection Prevention - Source voiceforip.com
- Taxonomy: European hornets belong to the family Vespidae and are closely related to other social wasps, such as yellow jackets and paper wasps.
- Biology: European hornets are characterized by their large size, with queens measuring up to 3.5 cm in length, and workers measuring around 2.5 cm. They build nests made of paper pulp in trees, shrubs, or other sheltered locations.
- Diet: Adult hornets feed on nectar and other sugary substances, while larvae are fed insects and other small prey.
- Stings: European hornets have a painful sting that can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Stings are typically delivered when the hornet feels threatened or its nest is disturbed.
- Prevention: To prevent stings, it is important to avoid disturbing hornet nests and to take precautions when working or spending time in areas where hornets are known to be present.
- Treatment: In case of a sting, it is recommended to remove the stinger and apply a cold compress to the affected area. Medical attention may be necessary if the sting causes a severe allergic reaction.
Understanding the biology and behavior of European hornets is essential for preventing stings and reducing the risks associated with these insects. Taking appropriate measures, such as avoiding nest disturbances and using protective clothing when necessary, can help minimize the chances of encountering and being stung by these wasps. By implementing these preventive measures, we can enjoy outdoor activities and environments where European hornets may be present with a reduced risk of painful and potentially dangerous stings.

Data Loss Prevention Deployment Specialist - Introduction - Source partneracademy.zscaler.com
European Hornets: Biology And Prevention Of Stings
The biology of European hornets is inextricably linked to the prevention of their stings. Understanding their life cycle, behavior, and nesting habits is crucial for developing effective strategies to minimize the risk of encounters and subsequent stings. The connection between biology and prevention is evident in several key areas:
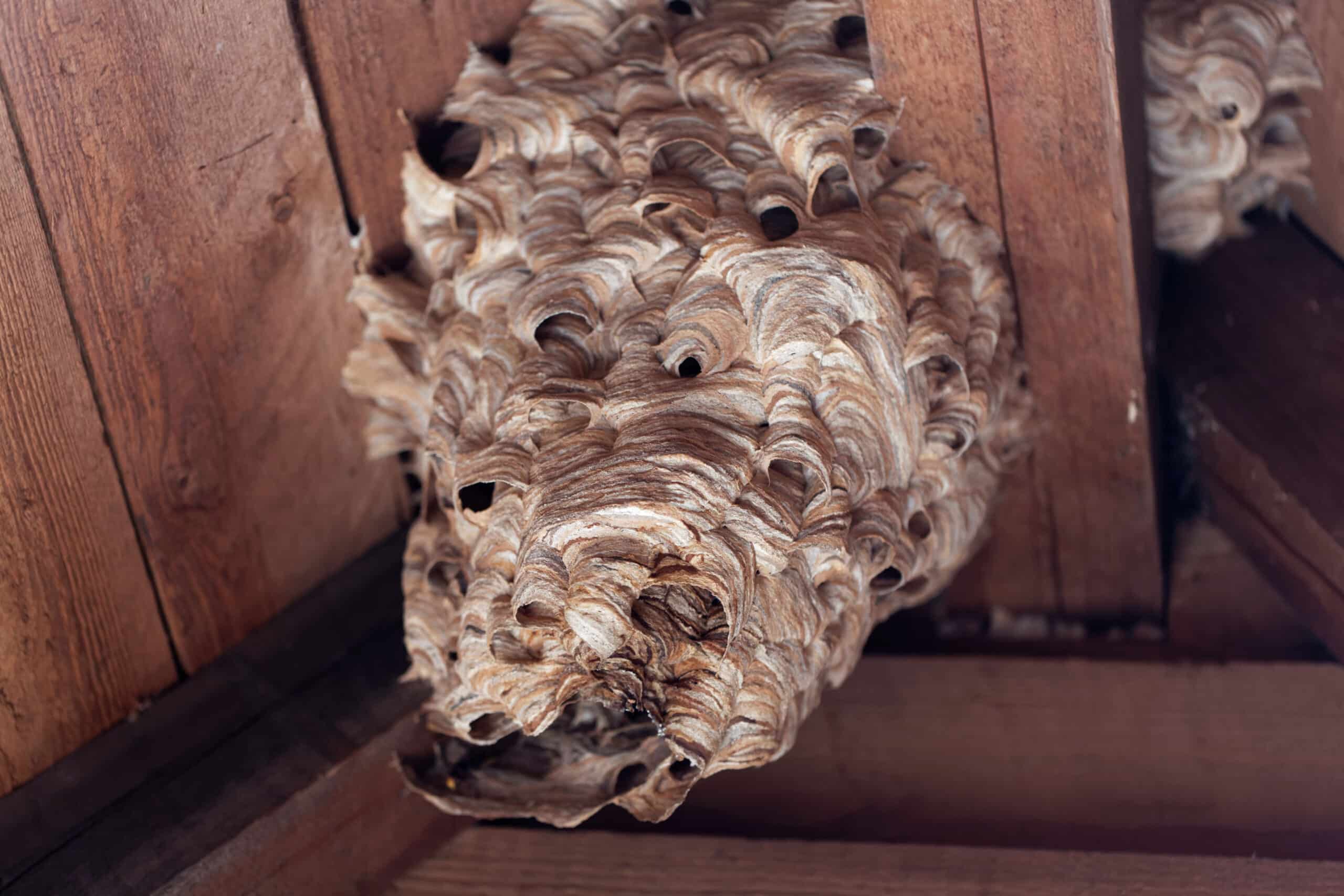

The Dangers of Hornets | Hornet Prevention | Modern Pest - Source www.modernpest.com
Firstly, knowledge of hornet biology allows for targeted prevention measures. For example, knowing that European hornets build their nests in enclosed spaces, such as tree cavities or attics, enables homeowners to seal up potential nesting sites, reducing the likelihood of close encounters. Additionally, understanding the hornets' foraging patterns helps identify areas of high activity, allowing individuals to avoid these areas during peak foraging times.
Furthermore, understanding the behavior of European hornets is essential for preventing stings. Hornets are generally not aggressive, but they will defend their nests if threatened. Sudden movements or loud noises near a nest can trigger an attack. By understanding these behaviors, individuals can take precautions such as avoiding disturbing nests and maintaining a safe distance when encountering hornets.
In summary, the connection between the biology of European hornets and the prevention of their stings is undeniable. By understanding their life cycle, behavior, and nesting habits, individuals can implement targeted prevention measures, such as sealing up potential nesting sites and avoiding areas of high activity. This understanding empowers individuals to minimize the risk of encounters and stings, ensuring a safer environment for all.
Table: Key Insights into the Connection between European Hornet Biology and Sting Prevention
| Biological Aspect | Prevention Implication |
|---|---|
| Nest location and construction | Seal up potential nesting sites |
| Foraging patterns | Avoid areas of high activity |
| Defensive behavior | Avoid disturbing nests and maintain a safe distance |
Conclusion
The exploration of European Hornets: Biology and Prevention of Stings has highlighted the profound connection between understanding the insect's biology and effectively preventing encounters and subsequent stings. By recognizing the hornets' nesting habits, foraging patterns, and defensive behaviors, individuals can implement targeted prevention measures to minimize the risk of interactions. This understanding not only enhances personal safety but also contributes to a harmonious coexistence between humans and these fascinating creatures.
As we continue to delve into the complexities of European hornets and their behavior, we can anticipate further advancements in prevention strategies. This ongoing exploration empowers us to protect ourselves while respecting the vital role that hornets play in our ecosystems.